Social media is buzzing with food and nutrition facts. As people are becoming more inclined towards health and food, words such as functional foods and superfoods are at the tip of everyone’s tongue. Healthy foodies and health enthusiasts are promoting the use of superfoods and functional foods. But do you know that there is a thin line of difference between both these popular terms?
If you are oscillating between functional and superfoods, read this blog to learn more about them.
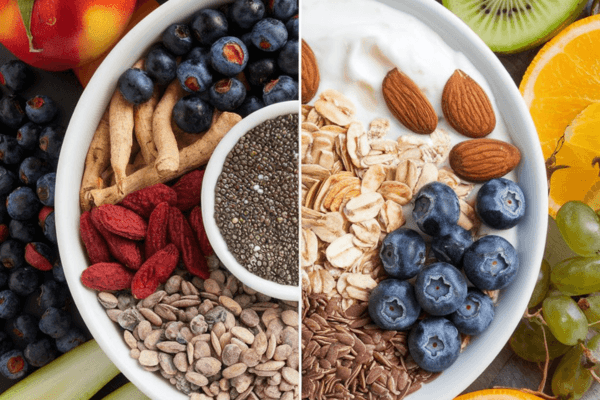
Superfoods vs. Functional foods
Both these terms are new labels for foods which have been consumed for many decades. Though there are no exact criteria that categorise both, here is a table to help you understand their similarities and differences:
| Superfoods | Functional foods |
| They are whole and natural foods with minimal processing | They may be natural, processed or fortified |
| They are nutrient-dense foods rich in micronutrients like vitamins, minerals, phytonutrients etc. | They are groups of food which in addition to nutritional benefits, provide other health benefits. |
| They do not usually have scientific backing | They have scientific backing to understand their functional health properties |
| Ex.: Berries, kale, salmon etc. | Ex. Lion’s mane, Ashwagandha etc. |
The concept of functional foods
Though all foods do have some amount of functional properties due to their nutritive value, smell and taste. Physiological analysis of functional foods has led to the development of functional foods.
In other words, functional foods are:
- Food of natural origin.
- Food which should and could be consumed on a daily basis.
- Food helps in regulating body processes and functions (ex. Preventing diseases, helping in recovery from diseases, Retarding ageing, and improving biological defense mechanisms).
*The definition of functional foods may vary based on the organisation
Functional food sources
There are many functional food varieties which have unique individualistic properties:
Plant-based sources
- Lion’s Mane – It belongs to the mushroom family. It is known by other names such as bearded tooth mushroom, pom pom mushroom etc. It improves neurological, cognitive and immune support.
- Ashwagandha – It is also called as the Indian ginseng. It is an adaptogenic herb which can improve immunity, and cognitive health and also has anti-inflammatory properties.
- Turmeric – Curcumin present in turmeric can improve brain function in addition to its anti-inflammatory, anti-cancer and antioxidant properties.
- Black tea – Black tea is made by creating an infusion of the leaves of Camellia sinensis. It is rich in epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG), theaflavins and thearubigins. Studies have shown that drinking black tea on a regular basis can help reduce the risk of heart disease.
- Moringa – Drumstick leaves or moringa can be used as an additive to food. It improves vitamin and mineral status while also preventing lipid oxidation.
Animal-based sources
- Dairy-based products – Milk is a rich source of micro and macronutrients. Though it is rich in calcium, fermented milk products have a special role in health. Such probiotic-rich milk products may have anti-carcinogenic, hypocholesterolemic and antagonistic properties.
- Fish – Fish is a rich source of omega-3 fatty acids. The current diet, being westernised, is deficient in omega-3 fatty acids. Consuming fish can play a role in correcting the imbalance of the omega-6:omega-3 fatty acids.
- Meat – Studies have revealed that meat by itself is not a risk factor for heart diseases, but rather the modern animal cultivation practices. Consuming learned meat can help lower cholesterol levels.
- Eggs – Eggs provide both essential and non-essential nutrients which can protect humans from degenerative processes.
Disadvantages of consuming functional foods - They are easily over-consumed.
- They are expensive.
- Some foods have misleading marketing claims.
- They may cause allergic reactions.
- They may interact with other medications
- They are not easily accessible.
- They are still undergoing research.
Tips to include superfoods and functional foods in the diet - Remember to include all colours of the rainbow (VIBGYOR – Violet, Indigo, Blue, Green, Yellow, Orange, Red) in the diet.
- Choose healthy cooking oils like avocado oil, coconut oil etc.
- Include good fats like avocado, eggs, nuts seeds etc.
- Use a lot of whole spices and herbs like cinnamon, turmeric etc. when cooking.
- Include herbal teas in the diet.
- Choose fresh, organic produce.
- Choose grass-fed meat and poultry, free-range eggs etc.
- Include minimally processed fermented foods like Greek yoghurt, sauerkraut, kimchi etc.
- Choose low-temperature cooking methods to preserve the nutritional value of food.
Does everyone need to consume functional foods?
No, everyone does not require functional foods. But just adding a few functional foods to your regular diet and consuming them consistently may help improve your health. However, remember to consult a doctor before opting to include functional foods to avoid side effects and understand the right dose.
Mayuri
Dietetic Researcher, Simplyweight